Accesibilidad, Digital Production
Omnichannel in Regulated Environments: Strategy to Healthcare Implementation
Igor Alvarez - Chief Innovation Officer

*This is the third article in our four-part series exploring omnichannel implementation in healthcare communication. Previously, we discussed the foundational concepts of true omnichannel and the necessary technical infrastructure. Now, let’s focus on practical strategies to successfully implement omnichannel initiatives within regulated healthcare settings.
Implementing an omnichannel strategy in healthcare comes with unique challenges that go beyond typical digital transformation efforts. While many organizations recognize the value of omnichannel approaches, execution often falters due to regulatory requirements, approval processes, and organizational silos.
This isn’t just a theoretical issue. A 2024 Accenture study revealed that 63% of pharmaceutical companies attempting omnichannel implementations didn’t achieve their expected outcomes.1 The gap between strategy and execution is significant, especially in regulated environments where new communication methods must navigate complex approval processes.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- Modular content approaches that streamline implementation while ensuring compliance
- Adapting agile methodologies for regulated healthcare environments
- Optimizing approval workflows to reduce time-to-market without compromising standards
- Real-world case studies demonstrating successful implementation strategies
Embracing Modular Thinking in Healthcare Communication
At the heart of successful omnichannel implementation in healthcare is modular thinking. This approach provides the flexibility, efficiency, and governance needed to execute complex communication strategies in regulated environments.
Beyond Component-Based Materials
Modular thinking isn’t just about creating compartmentalized materials. It involves understanding the context in which each content element will be used, the specific requirements of each scenario, and critically, the approval and governance processes that regulate these materials.
By developing content modularly, healthcare organizations can:
- Efficiently reuse and adapt content across various channels
- Simplify approval processes through standardized modules
- Accelerate time-to-market for new materials
- Create personalized experiences using approved content blocks
From Core Content to Omnichannel Delivery
Applying modular content in healthcare omnichannel strategies is transformative. Instead of crafting entirely new content for each channel, start with “core content” that can be adapted and delivered across multiple formats and platforms.
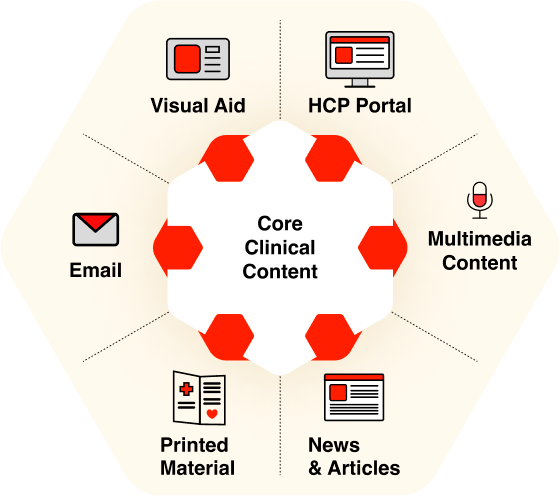
For example, a single core piece detailing a study, clinical information about a medication, etc. can be transformed into:
- Customizable visual aids for representatives
- Audio content for podcasts
- Printed materials for in-person visits
- Tailored email content
- News/Articles for external websites, being aware of the limitations of general-public communication
This approach ensures that scientific information remains consistent while being adapted for different contexts and channels, making the content accessible to more users across various formats and situations.
Adapting Implementation Methodologies for Regulated Environments
Traditional digital implementation methodologies often need significant adaptation for healthcare. We’ve developed specialized approaches that balance agility with regulatory compliance.
Regulated Agile: Combining Speed and Compliance
Traditional agile methodologies emphasize rapid iterations and continuous deployment—approaches that can conflict with the structured approval requirements of healthcare communications. However, modified agile approaches can be highly effective when tailored to regulatory constraints.
Key adaptations include:
- Compliance-integrated sprints – Embedding regulatory reviews within sprint cycles rather than treating them as external dependencies
- Modular approval pathways – Creating pre-approved component libraries that can be assembled in different configurations without requiring full re-approval
- Parallel workstreams – Designing implementation plans where technical development progresses while content undergoes regulatory review
- Validated automation – Implementing automated testing and validation processes that satisfy documentation requirements
Cross-Functional Governance Models
Successful implementation requires governance structures that unite traditionally siloed departments. Creating cross-functional teams with representation from regulatory, medical, marketing, and IT departments can significantly accelerate implementation while reducing compliance risks.3
Effective governance models establish:
- Clear decision authority across departments
- Standardized approval workflows
- Explicit documentation requirements
- Regular synchronization points
According to IQVIA’s ‘Time to Take Omnichannel Action’ white paper, pharmaceutical companies that implemented integrated governance models saw significant improvements in HCP engagement metrics, with an 8% increase in positive perception of information relevance and a 7% increase in satisfaction with cross-channel coherence between 2019-2023.2
Adapting Implementation Methodologies for Regulated Environments
Traditional digital implementation methodologies often need significant adaptation for healthcare. We’ve developed specialized approaches that balance agility with regulatory compliance.
Regulated Agile: Combining Speed and Compliance
Traditional agile methodologies emphasize rapid iterations and continuous deployment—approaches that can conflict with the structured approval requirements of healthcare communications. However, modified agile approaches can be highly effective when tailored to regulatory constraints.
Key adaptations include:
- Compliance-integrated sprints – Embedding regulatory reviews within sprint cycles rather than treating them as external dependencies
- Modular approval pathways – Creating pre-approved component libraries that can be assembled in different configurations without requiring full re-approval
- Parallel workstreams – Designing implementation plans where technical development progresses while content undergoes regulatory review
- Validated automation – Implementing automated testing and validation processes that satisfy documentation requirements
Cross-Functional Governance Models
Successful implementation requires governance structures that unite traditionally siloed departments. Creating cross-functional teams with representation from regulatory, medical,
marketing, and IT departments can significantly accelerate implementation while reducing compliance risks.3
Effective governance models establish:
- Clear decision authority across departments
- Standardized approval workflows
- Explicit documentation requirements
- Regular synchronization points
According to IQVIA’s ‘Time to Take Omnichannel Action’ white paper, pharmaceutical companies that implemented integrated governance models saw significant improvements in HCP engagement metrics, with an 8% increase in positive perception of information relevance and a 7% increase in satisfaction with cross-channel coherence between 2019-2023.2
Streamlining Approval Processes with Modular Content
One of the most significant advantages of modular content is its ability to transform the regulatory approval process—typically one of the most time-consuming aspects of healthcare communication.
The Master Document Approach
An effective strategy involves creating a “master document” containing all possible content variations, clearly delineating required compliance elements from optional components. This approach offers several benefits:
- Regulatory reviewers can approve the entire range of potential content variations in a single review
- Implementation teams can select which optional components to use while maintaining required elements
- Personalization becomes possible without requiring individual approval for each variation
This methodology is particularly valuable for global pharmaceutical companies managing content across multiple markets, allowing for local adaptation while ensuring central compliance requirements are maintained.
Mandatory vs. Optional Content Components
Clearly distinguishing between mandatory and optional content elements is fundamental to efficient approval processes. By structuring content with:
- Mandatory elements – Core scientific information, safety data, and regulatory statements
- Optional elements – Format variations, channel-specific adaptations, and targeting options
Organizations can maintain compliance while gaining significant flexibility in deploying content across channels. In practice, this might mean approving a core scientific message along with multiple presentation formats simultaneously, allowing marketing teams to select the most appropriate format for each channel without requiring additional approvals.
Personalization Within Regulatory Boundaries
Implementing personalization—a core advantage of omnichannel approaches—presents unique challenges in healthcare environments where every communication may be subject to regulatory scrutiny.
User Preference and Behavior-Based Adaptation
Preference-based personalization offers a compelling and compliant alternative. This approach:
- Begins with explicit preference capture (e.g., content format preferences, topic interests)
- Builds profiles based on observed channel and content engagement
- Uses these inputs to tailor which modules are presented to each user
This strategy provides meaningful personalization while maintaining a clear rationale for why specific content is shown to particular users—an important consideration for regulatory documentation.4
Automated Rule-Based Implementation
Implementing personalization in regulated environments benefits significantly from rule-based automation. By establishing clear, documented rules for how content adaptation occurs, organizations can provide regulators with transparency into the personalization process.
For example, a rule might specify that “HCPs who have viewed content on mechanism of action three times will be presented with advanced efficacy data in their next interaction.” This approach creates an auditable decision path that satisfies compliance requirements while delivering relevant content to users.
Case Study: Omnichannel Implementation During Communication Restrictions
The principles discussed above were tested during a challenging implementation for a global healthcare organization facing dual constraints—temporary restrictions on their primary communication channel (face-to-face visits due to COVID-19) and limitations on their standard digital tool.
The Challenge
- No consolidated channel for digital communication
- Inability to use established tools due to temporary restrictions
- Need for an immediate solution with a long-term improvement plan
- Requirement to maintain full regulatory compliance throughout
Our Implementation Approach
We deployed a modular implementation strategy with key elements:
- Assessment with step-by-step improvement plan – Establishing clear phases aligned with regulatory review cycles
- Temporary modular communication system – Creating a compliant interim solution using available approved components
- Agile content creation flow – Developing a process for rapid iteration with built-in approval checkpoints
- Progressive channel expansion – Starting with email, then methodically adding other channels
This modular approach allowed for:
- Rapid deployment of initial capabilities (under one month)
- Progressive enhancement as new approvals were secured
- Adaptation to changing regulatory requirements
- Continuous improvement based on performance data
The implementation delivered exceptional results:

- Expanded to 12+ Latin American countries
- Reached over 50,000 registered healthcare professionals
- Achieved 40% email open rates (well above industry average)
- Drove market share growth of 8% among less-visited doctors and 4% among regularly
visited ones
The key to this success was the modular implementation approach, which allowed for rapid initial deployment followed by systematic expansion. Each phase built upon approved components while adding new capabilities, creating momentum and demonstrating value that supported continued investment.
Implementation Best Practices for Healthcare Omnichannel
Based on our experience implementing omnichannel strategies in regulated healthcare environments, we’ve identified several critical success factors:
1. Design Systems Enable Modular Implementation
Developing a comprehensive design system—from typography and colors to well-structured components—creates the foundation for efficient implementation. A well-defined design system ensures:
- Visual consistency across channels
- Compliance with brand guidelines
- Simplified development of new materials
- Efficient updates when regulations change
The most effective design systems include specific components designed for regulatory requirements, such as standardized safety information displays, consistent adverse event reporting mechanisms, and templated important safety information sections.
2. Enable Non-Technical Content Creation
Successful implementation requires empowering content teams to create and adapt materials without constant technical intervention. By building modular systems with intuitive editing interfaces, organizations can dramatically accelerate content deployment while maintaining compliance.
The best implementations include:
- Simplified editing tools for non-technical users
- Pre-built templates with mandatory elements locked
- Clear visual indicators of editable regions
- Automated validation of completed content
3. Establish Clear Decision Rights and Workflows
Implementation friction often stems from unclear decision-making authority and approval pathways. Successful implementations establish explicit protocols for:
- Who owns final approval decisions at each stage
- Which changes require full reapproval versus limited review
- How conflicts between departments are resolved
- What documentation is required at each approval gate
4. Implement in Measured Phases
Rather than attempting a “big bang” omnichannel launch, the most successful implementations follow a phased approach that:
- Begins with core capabilities in high-value channels
- Establishes measurable success criteria for each phase
- Uses data from early phases to refine later implementations
- Progressively expands to additional channels and capabilities
This measured approach builds organizational confidence, demonstrates value incrementally, and allows for course correction based on real-world performance data.
Looking Forward: Measurement as Implementation Guide
Implementation and measurement are inherently linked in successful omnichannel strategies. As we’ll explore in our final article in this series, “Measuring Success: Data Analytics and Optimization in Healthcare Omnichannel,” the decisions made during implementation directly impact measurement capabilities.
Effective implementation should include:
- Clear tracking mechanisms for each channel interaction
- User identification strategies that respect privacy requirements
- Data collection points that capture meaningful behavioral signals
- Unified analytics that connect cross-channel activities
When these measurement considerations are built into the implementation from the beginning, organizations gain the ability to continuously refine their omnichannel approach based on real-world performance data.
Transform Your Healthcare Communication Strategy
At C/Edge, we understand the unique challenges of implementing omnichannel solutions in regulated healthcare environments. Our team brings deep expertise in both technical implementation and healthcare compliance, ensuring your communication strategy meets today’s demands while preparing for tomorrow’s challenges.
Contact us to discuss how we can help you implement an effective, compliant omnichannel strategy that delivers measurable results.
References
[1] Accenture. “The ‘new’ rules of healthcare provider engagement.” https://www.accenture.com/usen/insights/life-sciences/new-rules-healthcare-provider-engagement
[2] IQVIA. “Time to Take Omnichannel Action” https://www.iqvia.com/-/media/iqvia/pdfs/emea/library/whitepaper/time-to-take-omnichannel-action.pdf
[3] Dirsehan, T. (2025). Managing Customer Experiences in an Omnichannel World. Chapter 7: Customer Experience Management in Omnichannel Retailing.
[4] Mason, T., & Jarvis, S. (2025). Omnichannel Retail: Digital Connection Has Become Essential. Chapter 4: The Fundamentals of Loyalty.
